1 Species
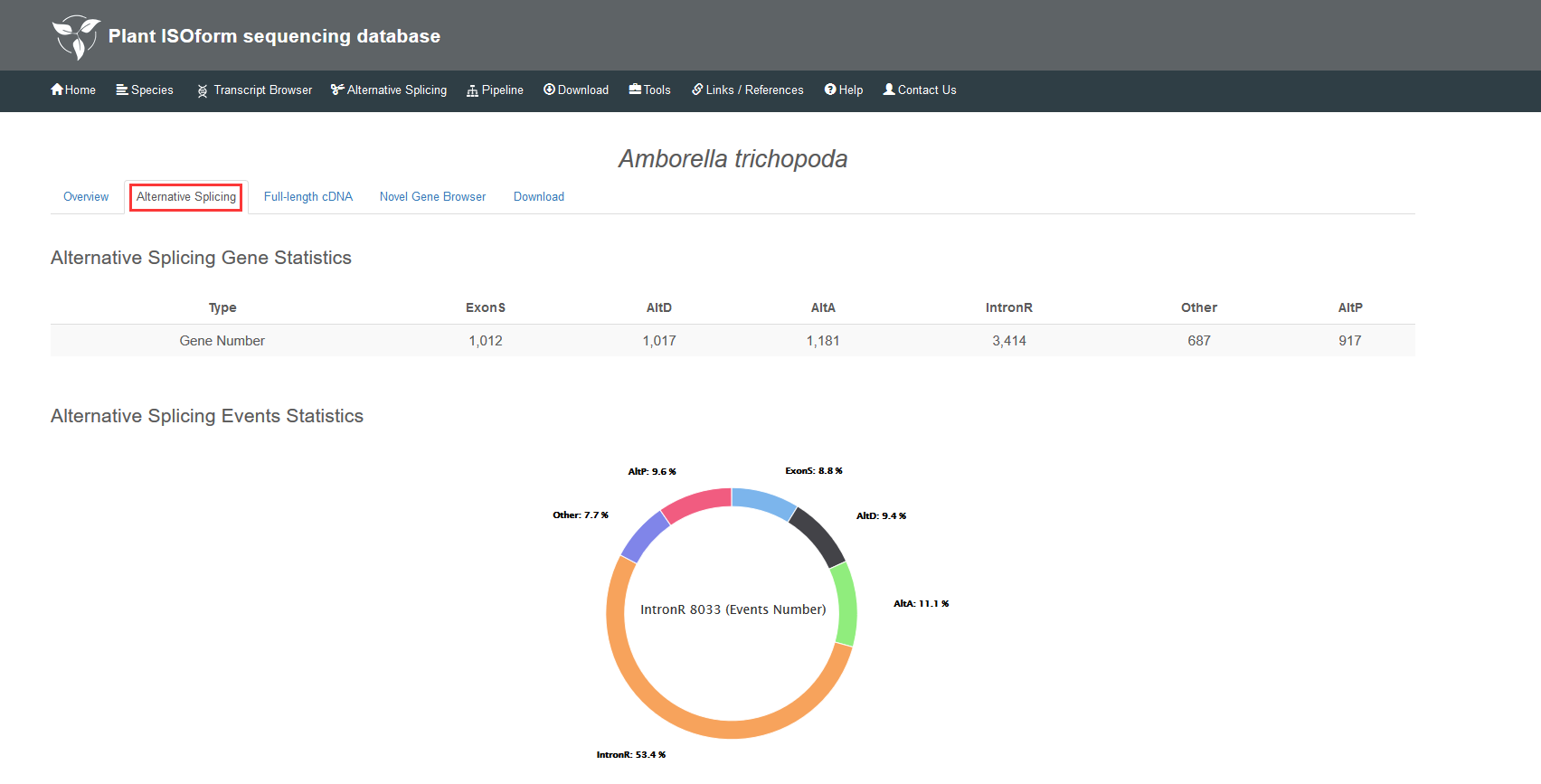
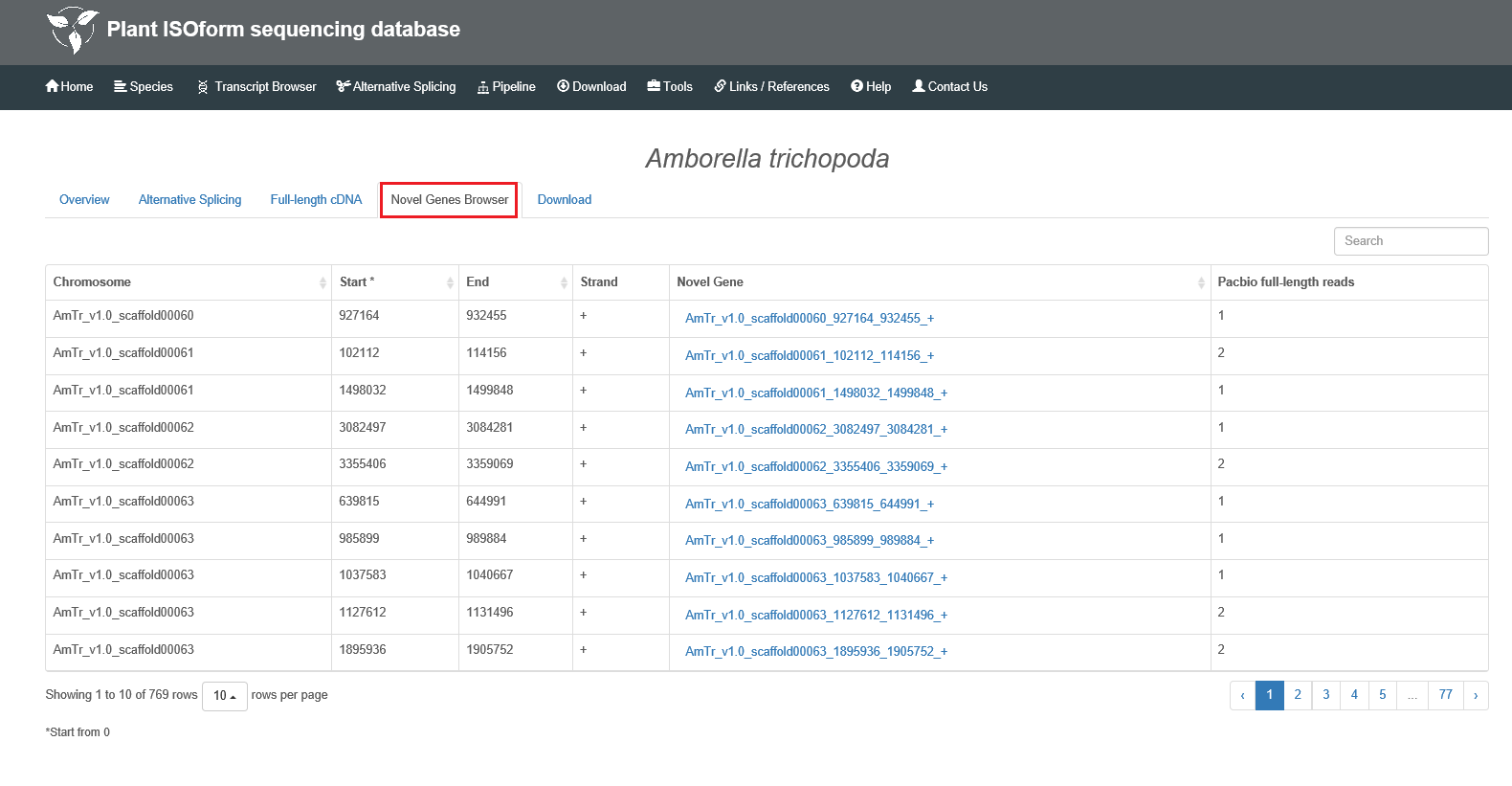
When you select one of 19 species, an overview including the information of reference genome and data is provided. The Alternative Splicing part supplies statistics for this species, and you can either get the number or the percentage of alternative splicing events. By switching to the full-length cDNA, the bar chart illustrates the results of GO annotation for the species. You can focus on any levels by clicking the corresponding legend on the right. The Novel Gene Browser is only valid for the species with reference genome and links to individual gene or transcript page.
1.1 Select species
1.2 Alternative splicing events and gene statistics
1.3 GO statistics

1.4 Novel Gene Browser
2 Transcript Browser
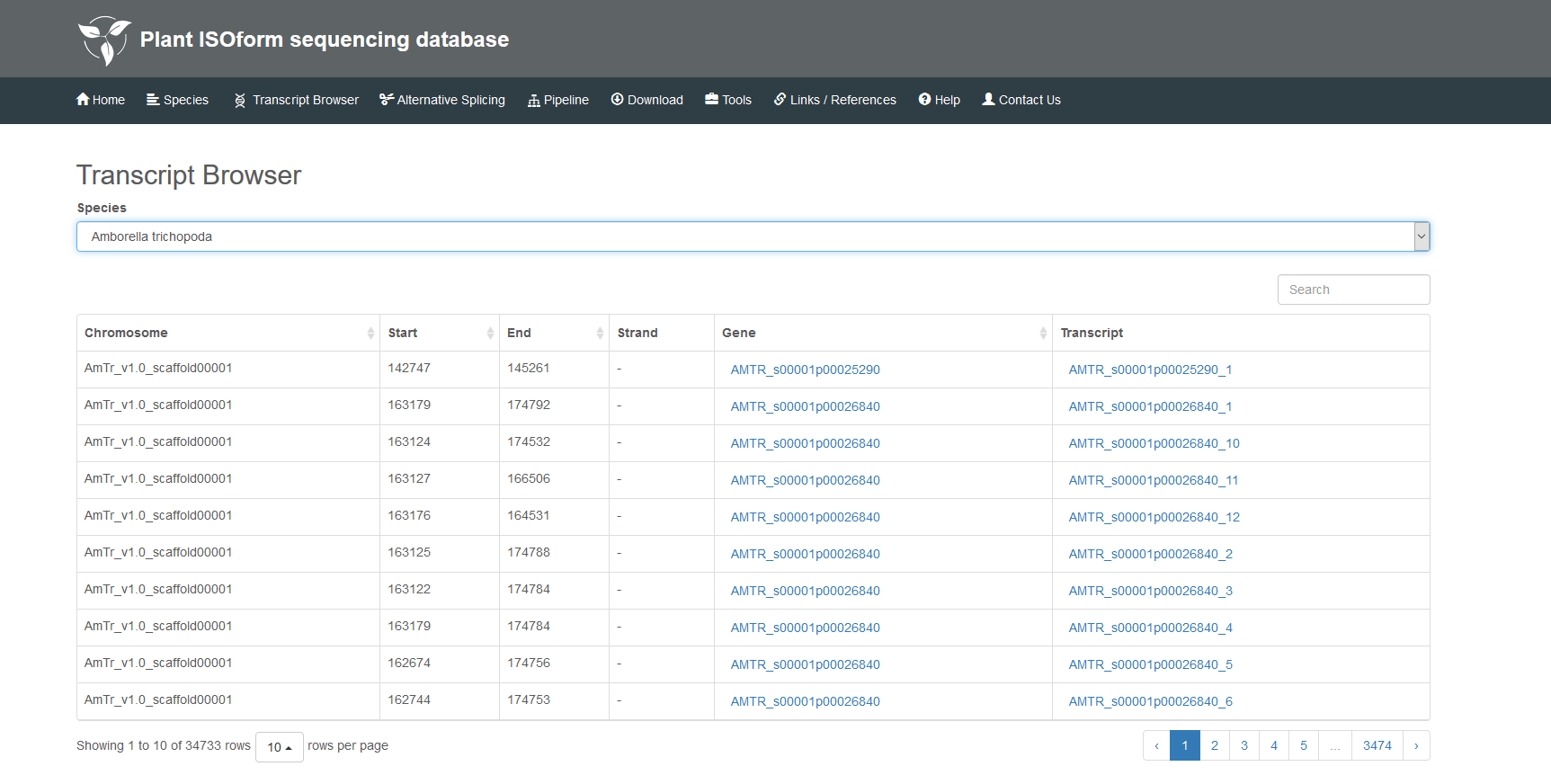
In this section, you can choose one species which you interest. For example, Allium sativum, the information of chromosomes, genes and transcripts are shown in this page. Then you can click on Gene or Transcript for its detailed information.The details are as follows:
2.1 Select species.
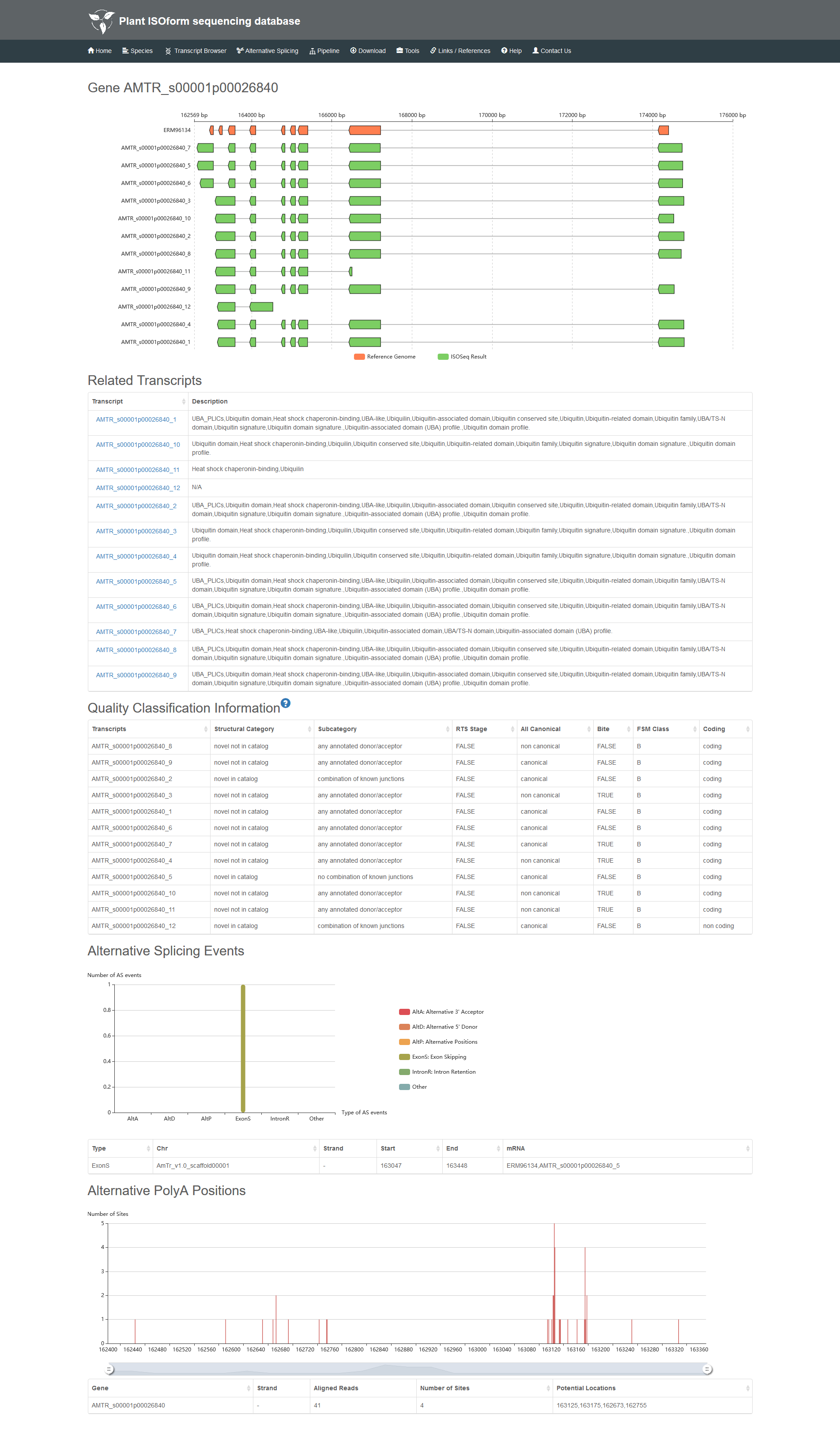
2.2 The details of gene.
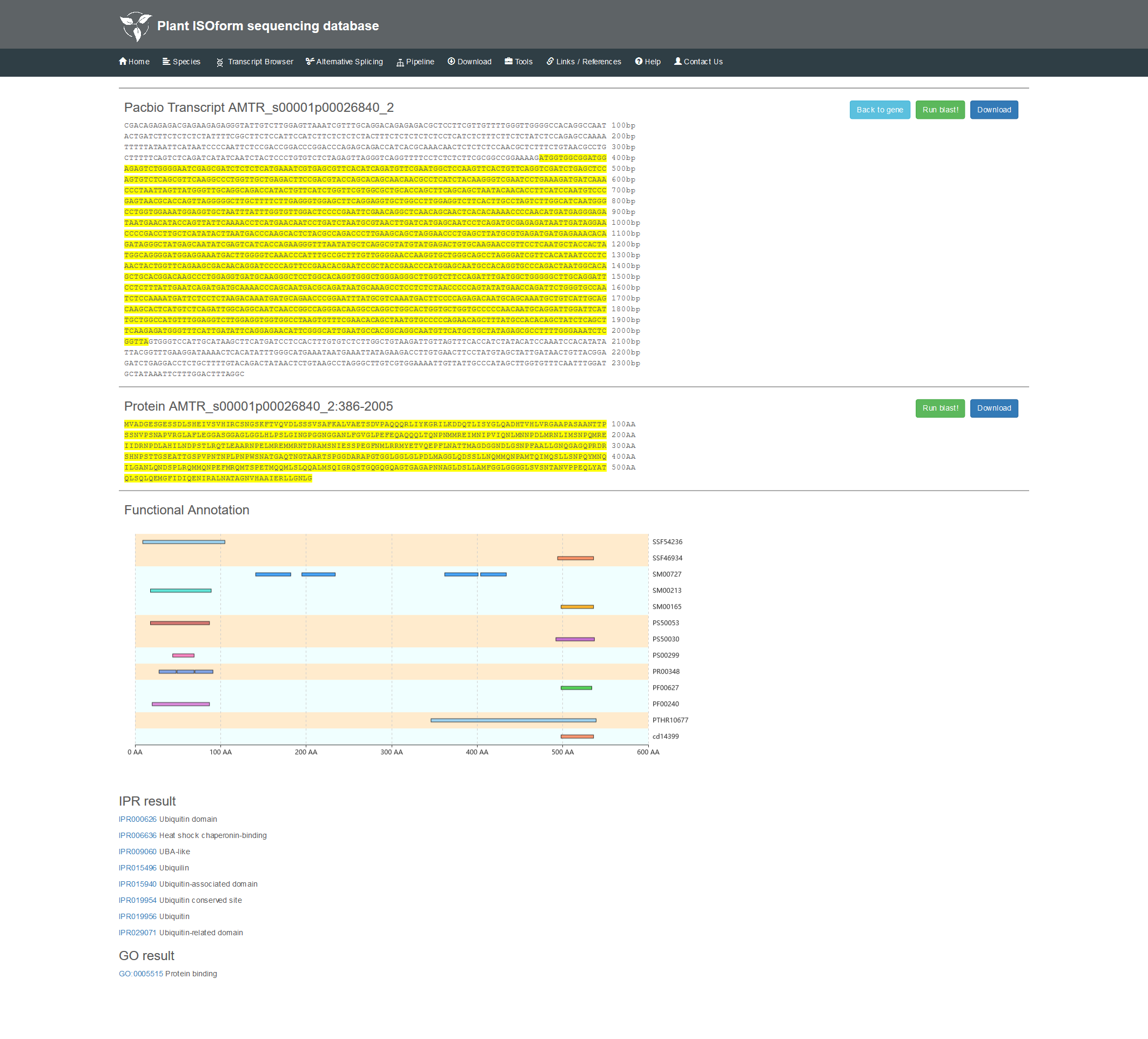
2.3 The details of transcript.
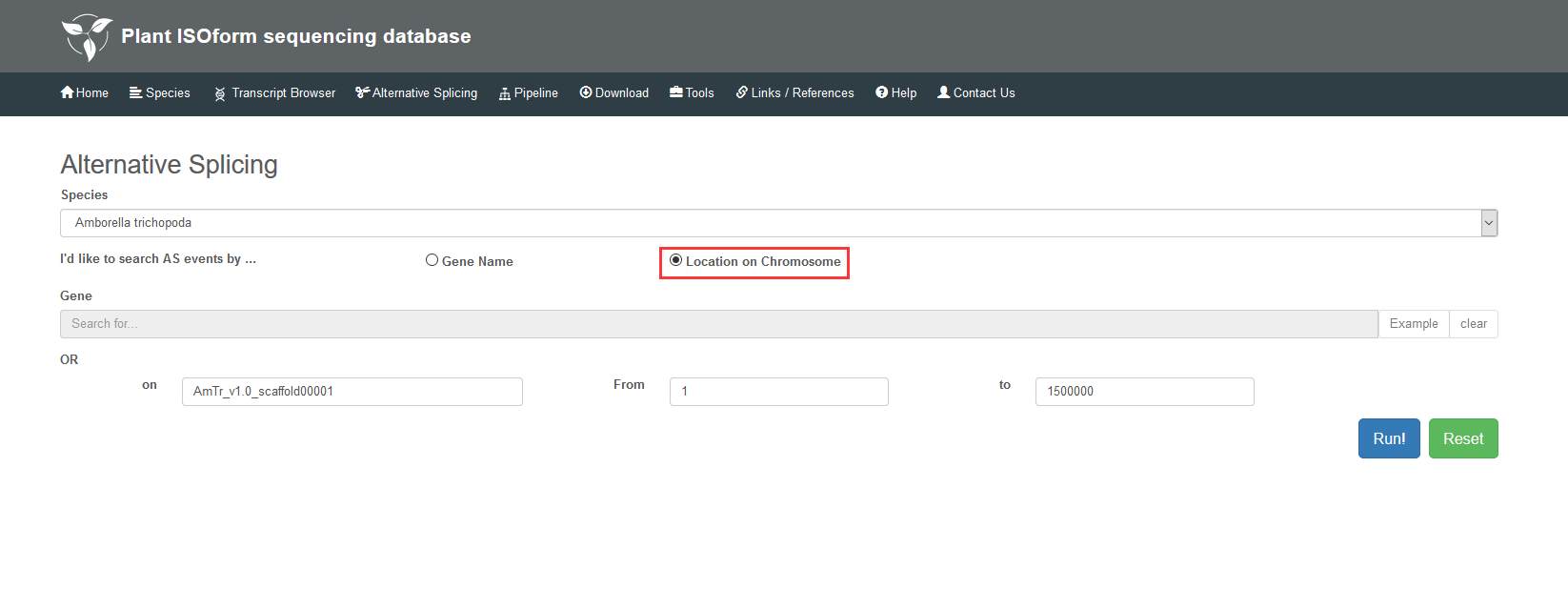
3 Alternative Splicing
You can find Alternative Splicing in two ways: Gene Name and Location on Chromosome. As to gene name, at first you choose a species, then select one gene you interest, finally click the “Run!” button. As to location on chromosome, you should input the number, the start and end sites of scaffold. The page will provide all the alternative splicing in this scaffold. Attentionally, you can only check alternative splicing through gene name for the species without reference genomes, such as 'Allium sativum', 'Astragalus membranaceus', 'Dipteryx oleifera', 'Nepenthes ampullaria', 'Nepenthes rafflesiana', 'Salvia miltiorrhiza'.
3.1 Search by gene name

3.2 Search by location on chromosome
4 Download
As to the species with reference genomes, you can download the sequences of full-length-cDNA, annotation of alternative splicing, sequences of novel genes and the information of Iso-seq gene model. As to the species without reference genomes, you can download the sequences of full-length-cDNA, annotation of alternative splicing, sequences of fake geneome and the information of Iso-seq gene model.

5 Tools
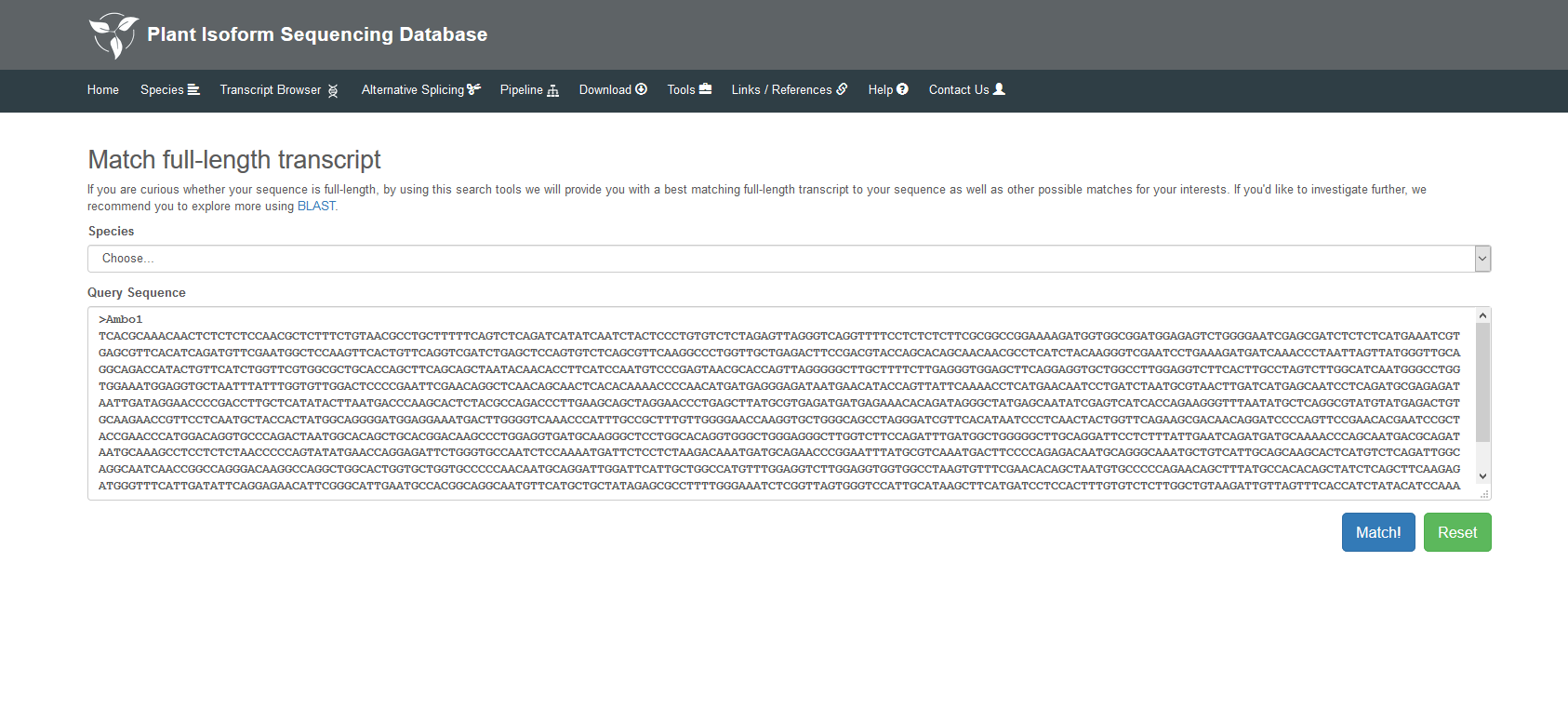
This section has four main functions: Functions Search, GBrowse, BLAST and Full-Length Match. In the Functional Search, detailed information of transcripts in each species can be found by InterPro accession, GO ID, Pfam accession, transcript name, gene name, etc., and the description of different transcripts is also displayed in this page. In the GBrowse, you can find transcripts generated by Iso-seq data, alternative splicing events and gene annotations. Detailed information of specific regions on the chromosome can be searched by transcript name, location or tracks. In the BLAST, you can obtain the summary of your sequence by selecting different types of BLAST, full-length transcript or reference genome of the species. In the Full-Length Match, we will provide you with a best-match full-length transcript to your sequence as well as other possible matches for your interest.
5.1 Functional Search
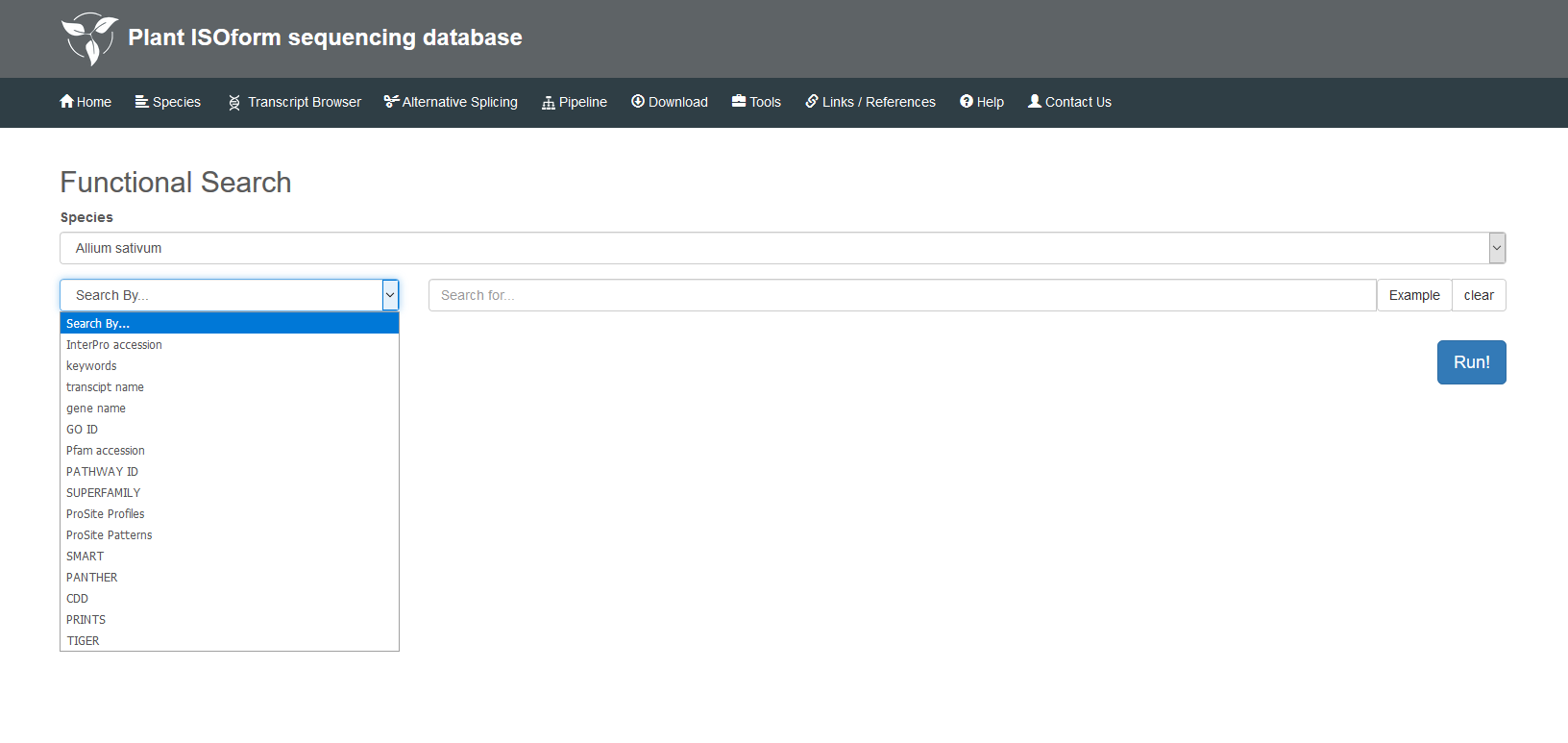
5.2 GBrowse
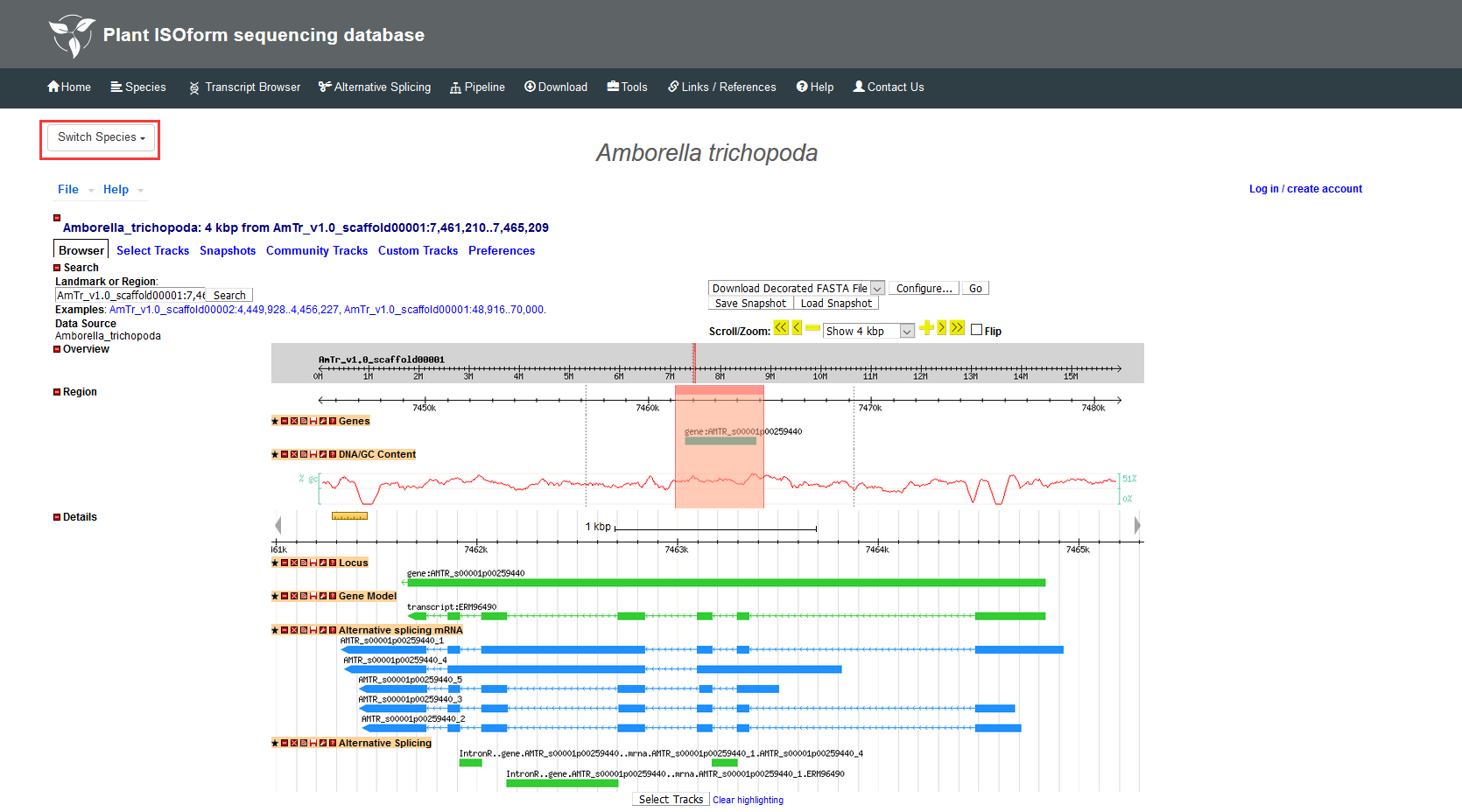
5.3 BLAST

5.4 Full-Length Match
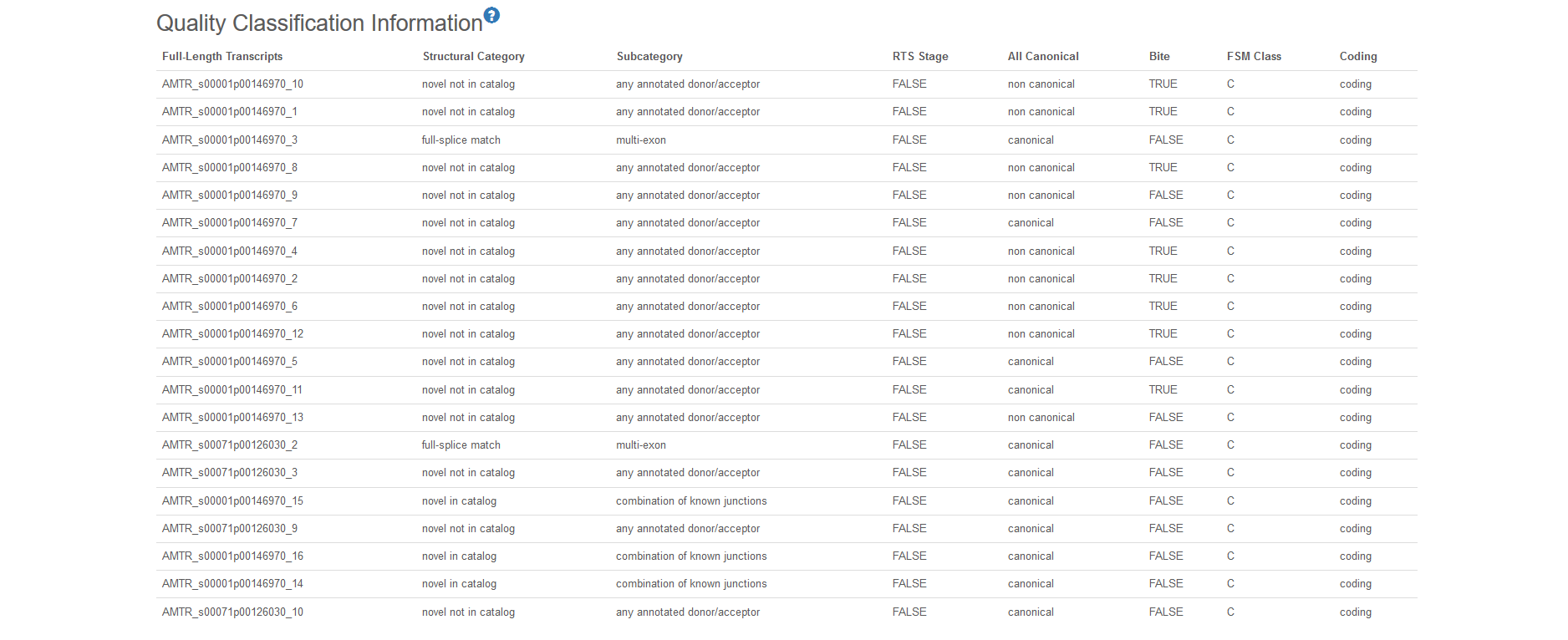
6 Quality Classification Information
SQANTI pipeline is used to estimate the quality of our transcripts, and these transcripts are illustrated by different parameters.
Structural category contains 9 types:
a) Novel Not in Catalog: The transcript which contains new combinations of already annotated splice junctions or novel splice junctions formed from already annotated donors and acceptors. b) Novel in Catalog: The transcript which uses novel donors and/or acceptors. c) Full Splice Match: The transcript which matches a reference transcript at all splice junctions. d) Incomplete Splice Match: The transcript which matches consecutive, but not all, splice junctions of the reference transcript. e) Genic: The transcript with partial exon and intron/intergenic overlaps in a known gene. f) Genic Intron: The transcript which lies entirely within the boundaries of an annotated intron. g) Intergenic: The transcript which lies outside the boundaries of an annotated gene. h) Antisense: The transcript contained PolyA overlaps the complementary strand of an annotated transcript. i) Fusion: The transcript which spans two annotated loci
Subcategory further classifies the transcript by splice junctions, which contain 10 types: a) any annotated donor/acceptor, b) multi-exon, c) combination of known junctions, d) 5 prime fragment, e) internal fragment, f) no combination of known junctions, g) not any annotated donor/acceptor, h) 3 prime fragment, i) mono-exon, j) mono-exon by intron retentions. All the transcript can be recognized easily by the subcategory tag.
RTS stage: Reverse Transcriptase switching (RTs) is an intrinsic property of RTs that allows them to jump within or across template positions without terminating DNA synthesis.
All Canonical: Splice junctions can be divided into canonical and non-canonical according to the two pairs of dinucleotides present at the beginning and end of the introns encompassed by the junctions.
Bite: The transcript has at least one junction labelled as bite.
FSM Class: This feature classifies the transcript according to the expression of other isoforms in the gene to which the transcript belongs. Transcripts belonging to genes that only express one isoform are classified as A. Transcripts belonging to genes that express more than one isoform but none is a FSM are classified as B. Transcripts belonging to genes which express more than one isoform and other isoforms and at least one is a FSM are classified as C.
Coding: Logical indicating if the transcript is predicted to have an ORF by GMST.